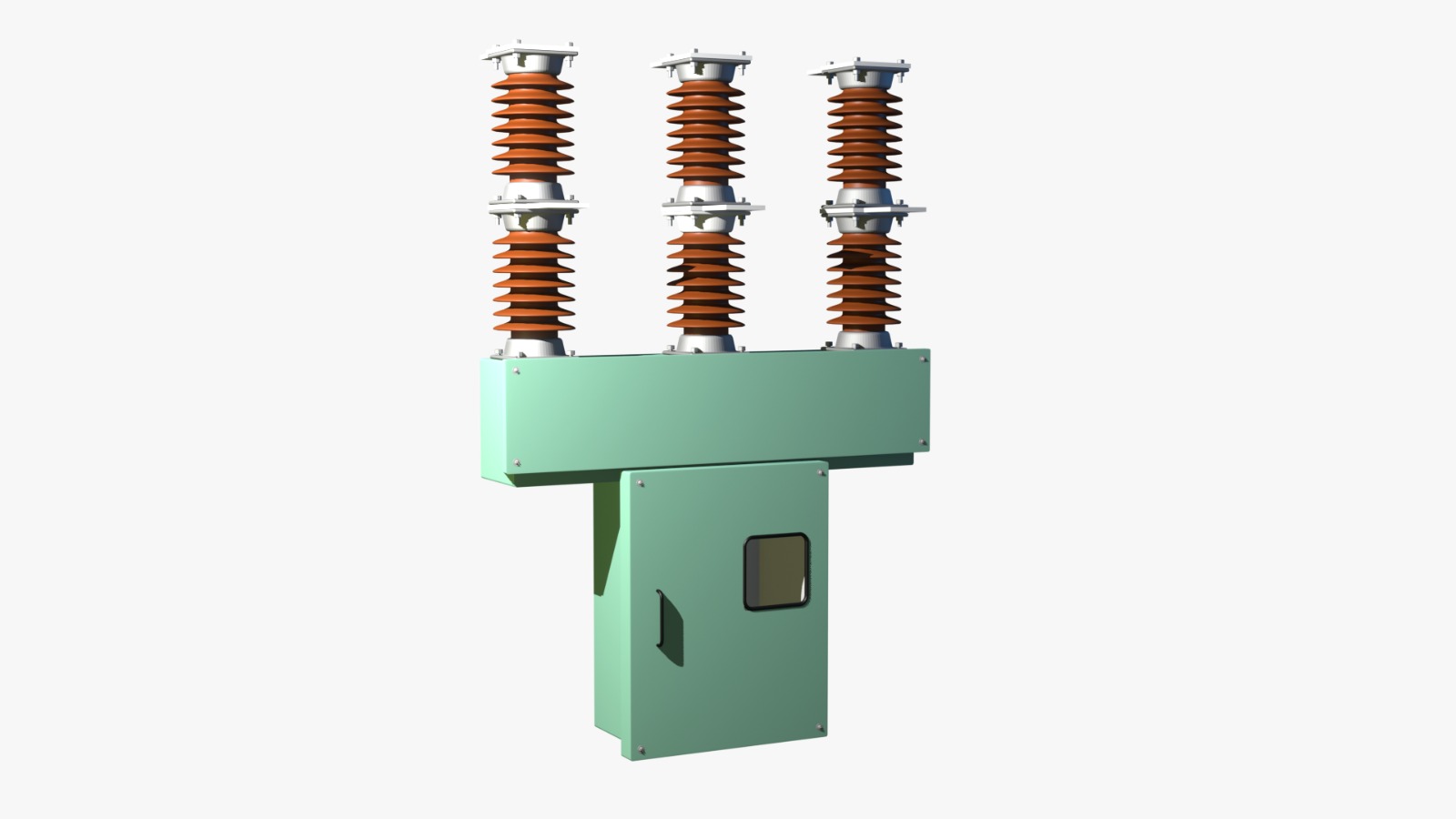
Introduction to Vacuum Circuit Breaker Technology
A vacuum circuit breaker is one of the most reliable and efficient types of circuit breakers used in modern electrical power systems. It operates by interrupting the electrical current in a vacuum environment, where the arc formed when the circuit breaks is quickly extinguished. The Vacuum circuit breaker has become a preferred choice for medium-voltage applications due to its compact design, long service life, and minimal maintenance requirements. This technology ensures the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems in industrial, commercial, and utility sectors.
Understanding the Working Principle of a Vacuum Circuit Breaker
The vacuum circuit breaker operates based on the principle that when electrical contacts separate in a vacuum, the arc generated between them is quickly extinguished because the medium (vacuum) has a very high dielectric strength. When the contacts part, a small arc forms as electrons and ions flow between them. However, since there are no gas molecules in the vacuum to sustain ionization, the arc quickly collapses. Once the arc is extinguished, the dielectric strength between the contacts recovers rapidly, allowing the vacuum circuit breaker to efficiently interrupt the current flow.
Main Components of a Vacuum Circuit Breaker
A vacuum circuit breaker consists of several essential components that ensure its reliable operation:
- Vacuum Interrupter – The core component where the actual current interruption occurs.
- Contacts – Made of special alloys that withstand the heat and arc energy during interruption.
- Operating Mechanism – Responsible for opening and closing the contacts.
- Arc Shield – Protects the vacuum interrupter’s internal walls from metal vapor during arcing.
- Housing and Insulation – Ensures proper insulation and mechanical protection.
These components work together to make the vacuum circuit breaker safe, efficient, and durable for high-performance electrical systems.
Advantages of Using a Vacuum Circuit Breaker
The vacuum circuit breaker offers numerous advantages over conventional circuit breakers:
- High dielectric strength: The vacuum medium provides superior insulation.
- Compact design: The compact construction of the vacuum circuit breaker makes it ideal for space-constrained installations.
- Low maintenance: Since there are no gases or oils involved, maintenance requirements are minimal.
- Long service life: The contact erosion is very low, allowing the vacuum circuit breaker to operate for many years without major wear.
- Eco-friendly: The vacuum circuit breaker does not use SF6 or other greenhouse gases, making it environmentally friendly.
Applications of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
The vacuum circuit breaker is widely used in:
- Industrial plants: For controlling and protecting medium-voltage circuits.
- Power distribution systems: Ensuring safe disconnection and isolation of faulty sections.
- Commercial buildings: Providing reliable protection against short circuits and overloads.
- Renewable energy systems: Protecting wind and solar power installations.
- Utilities: Used in substations and switchgear for medium-voltage network protection.
Because of its reliability and cost-effectiveness, the vacuum circuit breaker has replaced oil and air circuit breakers in most modern systems.
Types of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
There are several types of vacuum circuit breakers based on their design and operation:
- Fixed type: Installed permanently in switchgear panels.
- Draw-out type: Designed for easy removal and maintenance.
- Indoor type: Used in enclosed environments like substations and control rooms.
- Outdoor type: Designed to withstand environmental factors such as humidity and dust.
Each type of vacuum circuit breaker is designed to meet specific operational and environmental requirements.
Working Sequence of a Vacuum Circuit Breaker
When a fault occurs, the vacuum circuit breaker detects the overcurrent or short circuit and initiates the tripping mechanism. The operating mechanism rapidly separates the contacts inside the vacuum interrupter. The arc that forms is quickly extinguished because the vacuum medium does not allow ionization. After current interruption, the dielectric strength between contacts is restored almost instantly, ensuring the vacuum circuit breaker can withstand recovery voltage and prevent re-ignition.
Maintenance and Testing of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Although the vacuum circuit breaker requires minimal maintenance, periodic inspection ensures reliability. Key maintenance steps include:
- Visual inspection: Checking for external damage or contamination.
- Contact resistance testing: Ensuring the contacts have low resistance.
- Vacuum integrity testing: Verifying that the vacuum interrupter is sealed properly.
- Mechanical operation testing: Confirming smooth and reliable movement of the mechanism.
Proper testing guarantees that the vacuum circuit breaker continues to perform efficiently over time.
Comparison Between Vacuum Circuit Breaker and Other Breakers
Compared to oil, air, and SF6 circuit breakers, the vacuum circuit breaker stands out for its performance and environmental safety. Oil circuit breakers require frequent maintenance and have fire risks. Air circuit breakers are larger and less efficient at higher voltages. SF6 circuit breakers use a greenhouse gas that poses environmental concerns. In contrast, the vacuum circuit breaker is compact, clean, and requires minimal upkeep while providing equal or superior performance.
Future of Vacuum Circuit Breaker Technology
The vacuum circuit breaker is evolving with advancements in materials, automation, and monitoring technologies. Modern systems now integrate smart sensors for real-time condition monitoring and predictive maintenance. As power systems become more digitalized and eco-conscious, the vacuum circuit breaker will continue to play a critical role in ensuring safe and efficient power distribution.
Conclusion
The vacuum circuit breaker represents a milestone in electrical protection technology. Its ability to provide reliable, safe, and environmentally friendly current interruption makes it a vital component in modern power systems. From industrial plants to renewable energy grids, the vacuum circuit breaker delivers consistent performance, longevity, and sustainability. Understanding its working principles, advantages, and applications ensures that engineers and technicians can effectively utilize the vacuum circuit breaker for maximum system reliability and safety.